Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase AC induction motors is essential, especially when it comes to applications that require quick forward and reverse operations. This article explores what you need to know about using three-phase AC induction motors for instantaneous forward/reverse functions.
What is an Instantaneous Forward/Reverse Operation?
An instantaneous forward/reverse operation refers to a motor that repeatedly moves back and forth between two positions. For example, in a connector test fixture, the motor might insert and retract a connector to assess its durability. While this can be achieved with various types of motors—AC, brushless, servo, or stepper—the key factor is how quickly and accurately the motor stops when commanded to do so.
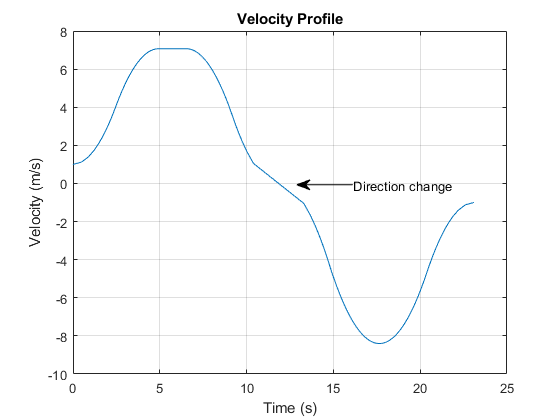
Credit: Mathworks
Â
Key Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase AC Induction Motors
1. Winding Design
The primary difference lies in the winding design. Three-phase motors have more balanced windings compared to single-phase motors. This balance affects the motor's performance and reliability during rapid direction changes. Below is a comparison of winding resistance values for two motors:
Â
| Power Supply (VAC) |
Motor |
Primary Winding |
Secondary Winding |
 |
| Phase U (Ohms) |
Phase V (Ohms) |
Phase W (Ohms) |
| Single-Phase 200/220/230 |
4IK25A-CW |
157.6 |
157.1 |
n/a |
| Three-Phase 200/220/230 |
4IK25A-SW |
179.9 |
179.9 |
179.9 |
Â
2. Performance Characteristics
Three-phase motors generally offer better speed-torque characteristics than single-phase motors. This means they can deliver higher starting torque, which is crucial for fast forward/reverse operations. When a single-phase motor reverses, it may take longer to reach rated speed due to lower torque. In contrast, three-phase motors can accelerate more quickly, making them ideal for high-speed applications.
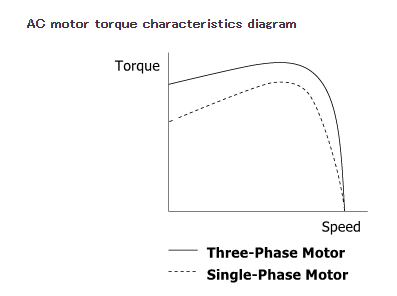
3. Starting Torque and Overrun
Single-phase motors typically don’t stop immediately unless equipped with a braking system. This can lead to significant overrun, which can interfere with the "instantaneous" aspect of the operation. Three-phase motors, on the other hand, provide higher starting torque and are better suited for these applications.
Â
| TIP #1: Stop a Three-Phase Motor Before Reversing Direction |
|
To ensure longevity and prevent damage, always allow the motor to come to a complete stop before reversing direction. Here’s why:
- Gear Damage
- Risk of Power Short Circuit
Gear Damage
Switching direction too quickly can cause gears to wear out faster. If the load continues to rotate while the motor tries to reverse, this can create stress on the gearhead.
Risk of Power Short Circuit
The wiring configuration for single-phase and three-phase motors differs. A three-phase motor requires a special switch to avoid short circuits, unlike a single-phase motor which only needs a simple SPDT switch.
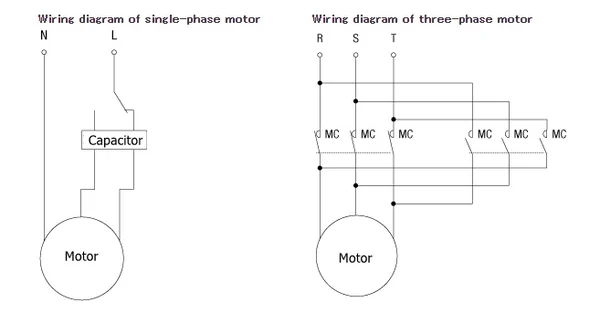
Differences in Wiring:
Single-phase motors use a capacitor to simulate a polyphase supply, while three-phase motors require a specific type of switch to avoid power shorts.
|
Â
Brake Frequency Considerations
Brake frequency is limited by temperature rise, which is influenced by inrush current. Frequent cycling can increase heat, reducing motor lifespan. It’s recommended to allow at least 2–4 seconds between cycles, depending on the motor size.
Â
| TIP #2: Use an Inverter |
|
Using an inverter (VFD) simplifies control of three-phase motors, enabling smoother forward/reverse operations. Oriental Motor offers models like the KIIS series, designed specifically for VFD compatibility.
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, 'd411f674-af9e-49e1-ba10-30a6d710f3bc', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, 'd411f674-af9e-49e1-ba10-30a6d710f3bc', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
|
Â
Speed-torque curves show how different motor and VFD combinations perform under various conditions. These graphs help engineers select the right components for their application.
Â
Finally, remember that while any motor can perform forward/reverse operations, the level of precision and speed depends on the motor type and control method. Three-phase motors are often preferred for their efficiency and performance in such tasks.
Oriental Motor provides a wide range of AC induction motors, including single-phase, three-phase, and specialized models like electromagnetic brake motors. Whether you're looking for constant speed or variable speed control, there's a solution to fit your needs.
Please subscribe to our blog for more insights and updates on motor technology and applications.
Â
Slewing Motor, Tower Crane Spare Part,Slewing Mechanism,Slewing Reducer,Slewing Bearing,Tower Crane Slewing Motor



