Discover the differences between stainless steel and carbon steel in terms of their properties and characteristics, which make them suitable for various applications. The table below provides a concise overview of both materials. Differences Between Stainless Steel and Carbon Steel Below are key points regarding the heat resistance of stainless steel and carbon steel. This will give you a summary of their heat resistance under different conditions and temperatures. SS vs CS Heat Resistance Stainless Steel Carbon Steel The following table provides detailed information on how both materials can be machined and welded, including the required speeds, tools, treatments, or conditions. Machinability and Weldability of Stainless Steel vs Carbon Steel Carbon steel contains up to 2.1% carbon by weight, making it stronger and more durable. The higher the carbon content, the harder and more durable the steel becomes after heat treatment. In contrast, stainless steel has a lower carbon content, making it less hard than carbon steel. Carbon Steel vs Stainless Steel Strength The table below provides details on how chromium content affects the properties of both materials and the benefits chromium provides. Chromium Content in SS and CS The following information explains why carbon steel is prone to rust when used in humid conditions. Why Is Carbon Steel Prone to Rust? What Makes SS Rust-Resistant? Hardness and Melting Points of Carbon Steel vs Stainless Steel Characteristics of Carbon Steel Characteristics of Stainless Steel Advantages of Stainless Steel Advantages: Advantages of Carbon Steel Advantages: Price Comparison of SS vs CS Carbon Steel vs Stainless Steel Properties Chemical Composition of Carbon Steel Factors to Consider When Choosing Stainless Steel or Carbon Steel Drymix Mortar admixtures has wide range of products, including HPMC, MHEC, RDP, HPS, PVA. Drymix Mortar Admixtures,Calcium Formate,Lignocellulose,Potassium Formate Santo Chemical Limited , https://www.santchem.com
Table of Contents
Feature
Symbol
Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel
Composition
Corrosion Resistance
Strength

Hardness

Weldability
Cost

Ductility

Thermal Conductivity
Finish

Hygiene

Lifespan

View Heat Resistance of SS vs CS Grades

Refer to Machinability and Weldability of Carbon and Stainless Steel
Features
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Machinability
Easily machined
Harder to machine
Weldability
Good welding capabilities
More challenging
Tool Wear
Tools last longer
Tools wear out quickly
Welding Processes
Versatile with various methods
Requires specific techniques and fillers
Cutting Speed
Higher speeds possible
Lower speeds needed
Surface Finish
Good finish achievable
Harder to maintain a good finish
Heat Affected Zone
Less prone to distortion
More prone to distortion; needs careful heat management
Post-Weld Treatment
Less critical
Often requires treatment to prevent issues
Carbon Steel is Stronger and More Durable Than Stainless Steel
Tensile Strength
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Low carbon steel
Medium carbon steel
Alloy steel
Austenitic Stainless Steel
Martensitic Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Ferritic
60,000 to 80,000 PSI
100,000 to 120,000 PSI
150,000 PSI
72,000 to 115,000 PSI
72,000 to 160,000 PSI
65,000 to 87,000 PSI
Carbon Steel Tends to Have Less Chromium Content Compared to Stainless Steel
Feature
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Chromium Content
Contains less than 1% chromium
Contains at least 10.5% chromium
Corrosion Resistance
Less corrosion resistance due to lower chromium content
Higher chromium content enhances resistance to rust and corrosion
Formation of Chromium Oxide Layer
Limited or no protective chromium oxide layer
Forms a thin, protective chromium oxide layer that prevents rusting
Carbon Steel is More Susceptible to Rusting When Exposed to Moisture
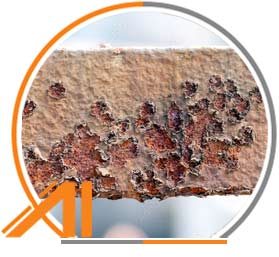

Feature
Brinell Hardness
Melting Points
Stainless Steel
Type 304: 201 MPa
1450°C
Ferritic Stainless Steel
Grade 430: 180 MPa
1450°C
Martensitic Stainless Steel
Grade 440C: 270 MPa
1450°C
Carbon Steel
Low-carbon steel
120 MPa
1450°C
High-carbon steel
200 MPa
1425-1540°C


Type of Steel
Cost Comparison
Considerations
Stainless Steel
More expensive than low or moderate-carbon steel.
Best for applications needing corrosion resistance and high performance.
High-Carbon Steel
More expensive than stainless steel.
Used for applications requiring high hardness and strength
Low/Moderate-Carbon Steel
Less expensive than stainless steel
Cost-focused applications (where cost is a priority and corrosion is less of a concern)
Property
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Tensile Strength
270-2100 MPa
200-200 MPa
Melting Point
1425-1540°C
1400-1510°C
Hardness
120-300 HB
140-400 HB
Density
Low
High
Corrosion Resistance
Low
High
Maintenance
High
Low
Durability
Less
High
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
10-12 * 10-6/°C
10-17 * 10-6/°C
Factor
Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel
Cost
More expensive
Less expensive
Corrosion Resistance
Superior resistant
Less resistant
Strength and Hardness
High strength
Can be heat-treated for hardness
Maintenance
Low maintenance
Requires regular maintenance and protective coatings
Low Carbon Steel
0.05-0.15
Medium Carbon Steel
0.3-0.5
High Carbon Steel
0.6-1.0
Ultra-High Carbon Steel
1.25-2